What is a Manufacturing Specification?
First things first, what does a manufacturing specification entail? Manufacturing specifications are all of the information you need to make something – and with a capital expenditure this big, there’s a lot at stake if you don’t get it right.
Think about your typical manufacturing workflow. What specifications does that include? Likely materials, machinery, quality control and conformance standards, production steps, and product/package designs. All of that information is captured and linked to a finished good to create a specification document.
What is the Difference Between a Manufacturing Spec and a Product Spec?
Manufacturing specs include a lot of information about products, so where do you draw the line between the two?
Manufacturing specs include product specifications, but don’t necessarily capture the finished good in its entirety. These technical specifications detail the materials, processes, and standards required during manufacturing. For example, if the manufacturer isn’t responsible for producing the labeling, that information wouldn’t be a part of that manufacturing spec. Similarly, construction specifications would not be included unless they are directly relevant to the manufacturing process.
On the other hand, product specifications include all information surrounding a finished product (not all of which are directly relevant to the manufacturing process, differentiating the two). However, these specs exist symbiotically, meaning you need information from one to complete the other. The best practice is to link this information together digitally, so you avoid having to constantly sift through data and can rest assured you have all the information you need to do your job.
Benefits of Manufacturing Specification
Manufacturing specificationsare a set of written specification documents entailing the product’s blueprint, such as the design, raw materials, and manufacturing processes.
Having the manufacturing specifications in place offers various benefits. Here are a few of them:
1. Quality Assurance
Manufacturing specifications allow manufacturers to follow required quality protocols at each stage of the product development process without deviating from the compliance and cost parameters. Manufacturers can specify the type of raw material to be used as well as tolerance levels to ensure their finished product checks out every quality filter. Specifying these thorough details helps maintain consistent quality and compliance.
2. Cost Management
Manufacturers can leverage manufacturing specifications to define cost ceilings for raw materials and manufacturing processes so that they don’t overspend in areas that are irrelevant to their bottom line, keeping the overall cost in check without sacrificing quality.
3. Compliance
Meeting compliance is a major challenge that manufacturing specifications can solve. Manufacturers can define safety, performance, and compliance requirements to make sure their final products meet internal and regulatory standards. Manufacturing specifications also offer an easy provision to accommodate ever-evolving compliance requirements.
4. Consistency across production lines
Manufacturers who manage multiple facilities can define the exact design and material specifications to make sure the final product is built to the desired standards across independent production lines.
Key Components of a Manufacturing Specification
Manufacturing specification is a blueprint entailing different processes and components involved in product manufacturing. A manufacturing specification is like a template that can be replicated for manufacturing products with the same quality and consistency. Let’s look at some of the key components of a manufacturing specification.
Product Design
Design is the lifeblood of a product manufacturing process. It is important to get the design made and implemented correctly to avoid product errors and recalls down the line. The design specifications include dimensions, materials, tolerance levels, and other features of the product. Design professionals often represent these specifications in the form of 3D models or drawings using CAD tools.
Materials
The materials used in the manufacturing process determine the product’s life, cost, and other physical attributes. This aspect of manufacturing specification outlines the type of raw material to be used, its physical and chemical properties, quality grades, certifications, etc. A comprehensive software toolkit can assist in managing these specifications efficiently. This section may also specify the material suppliers so that manufacturers can ensure ethical, cost-effective, and sustainable sourcing practices.
Manufacturing Processes
Every product passes through a series of processes before reaching the end of the production line. The manufacturing processes clearly define the sequential stages of production as well as the time and cost associated with each one of them. The manufacturing processes may also outline the specific techniques, equipment, and testing requirements at each stage of production.
Quality Control Measures
Every manufacturer emphasizes quality control measures to ensure their product meets regulatory compliance and internal quality standards. A product failing to meet these industry standards may be subject to recall or failure. The Quality Control Measure defines the testing and inspection protocols that must be followed to the letter. Moreover, it also defines the frequency of tests, acceptance criteria, substitutions, and corrective actions for quality assurance and to reduce the likelihood of defects.
Packaging and Labeling
Packaging and labeling is the final stage of the production process. This aspect of manufacturing specification outlines the following:
- Type of packaging material to be used for the final product
- Product labeling requirements
- Handling and Storage instructions
- Regulatory compliance for certain markets
Bill of Materials
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a list of materials and processes required to manufacture a product. This comprehensive list also helps manufacturers to determine production costs and make revenue-critical decisions.
BOMs are an important part of the manufacturing industry, helping decision-makers to ensure all the necessary materials and equipment required for production are available as and when needed. This comprehensive list also supports effective procurement planning and management.
From part names and part numbers to product descriptions and required quantity, everything that goes into building a product is included in the Bill of Materials.
Creating BOMs manually can take a lot of time and exhaust your valuable resources. Instead, you can use specialized software to quickly create BOMs and make adjustments when necessary. With BOMs in place, you can always rest assured that what you need will be available at your beck and call without the risk of material wastage or supply chain delays. As a result, you will be able to run smooth and profitable manufacturing operations.
Your Solution to Creating and Managing Manufacturing Specs
1. Understand Your Manufacturing Capabilities
Before creating manufacturing specs, it’s important to know your factory’s capabilities; i.e. what you can and can’t produce. For smaller-scale factories, this knowledge might be readily available by taking a walk around the plant floor. But for most manufacturing plants, it’s hard to know off-hand exactly what tooling you have available or what your maintenance schedules are.
This is where a smart factory comes in handy. A smart factory is a digital replica of your plant and machinery. It includes detailed specifications for machines, parts, lines, sub-assemblies, and more.
The good news?
Due to limitations in production capabilities, manufacturers are often able to clone and reuse foundational specs for new products, effectively specifying the necessary requirements without starting from scratch. This means spending less time entering data and more time making amazing things. By digitizing all of this information, you have everything you need to know about your plant at your fingertips, enabling you to make faster, more informed decisions, not to mention, accelerate manufacturing spec creation.
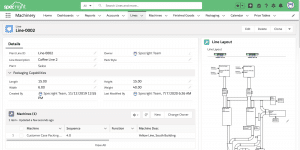
2. Create Your Project Workflow
The next step in creating manufacturing specifications is to build out your project workflow, ensuring all steps are clearly defined in written specifications.. Start by mapping out all of the steps in the manufacturing process. If you already have a smart factory created, you can easily plug and play product specifications with associated machinery specifications. This will help you gain a high-level understanding of what exactly will go into your manufacturing specs.
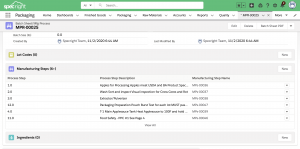
3. Spec Out the Manufacturing Process
Once you’ve got a basic template for your manufacturing process, you can start filling it in with manufacturing specs. Each step of the process will become a manufacturing spec. For example, MPs-00047 (below) includes detailed specs on how to perform that step. The spec is then linked to a manufacturing process and that process is linked to the finished good.
Manufacturing steps are the perfect opportunity to link machine and plant information. If it’s already digitized via a smart factory, this linkage is as easy as the click of a button.
Pro Tip: Manufacturing specs also enable high-level process monitoring. These specs can be used to paint a more complete picture of production, linking to data like:
- Work Orders/Customer Information
- WIP (work in process)
- Quality Control and Conformance
- Product Development
- Inventory
Your Solution to Creating and Managing Manufacturing Specs
At a time when many consumers and end-users are demanding greater transparency and traceability, such as ingredient quality or sourcing information, specification management is an invaluable tool for manufacturers.
Specright’s Specification Data Management™ software is helping to lead the charge by managing the complexities of manufacturing at the spec level. From a supply chain management perspective, Specright allows manufacturers to trace a digital thread of data throughout the supply chain to see where products are being sourced, where delays or bottlenecks are occurring, and other valuable information that can inform their operations.
To learn more about Specification Data Management, download our ebook or reach out to a member of our team.
Explore More Blogs
Get Started
With Specright’s Solution Suite, you can digitize, centralize, and link your specification data to drive efficiencies, intelligence, traceability, and collaboration within your organization and across your supply chain network.




