In the realm of business management, two critical systems often come into play: Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). Both serve distinct yet complementary roles in the operational success of companies, especially in industries like food and beverage, consumer products, chemicals, and life sciences. PLM focuses on managing a product’s lifecycle from conception through design and manufacturing to service and disposal, ensuring innovation, quality and regulatory compliance at every stage. Conversely, ERP integrates various functions such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing into a unified system to streamline processes and improve efficiency. While PLM emphasizes product development and innovation, ERP ensures operational excellence and resource optimization.
When examining the evolution of ERP and PLM technologies, ERP revolutionized the industry in the 1990s as companies sought to enhance efficiency in managing finance, manufacturing, and supply chain operations. However, the beginnings of this revolution trace back to the 1960s with the advent of solutions designed for inventory control. In the 1970s, these solutions evolved into Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems, which incorporated production scheduling and planning. ERP emerged as an extension of these capabilities, unifying business processes such as finance, HR, sales, and procurement.
What is PLM?
PLM began gaining attention from product manufacturers with the development of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems, which revolutionized product design by enabling digital creation and modification. Increasing product complexity also contributed to the growing interest in PLM. Initially adopted by the discrete manufacturing sector, PLM’s predecessor was Product Data Management (PDM), which provided a centralized repository for storing and managing complex product information. In the early 2000s, PLM systems evolved, integrating PDM with other critical functions such as collaboration, project management, and process control to manage the entire product lifecycle from conception to disposal. With the rise of digital technologies, PLM systems began incorporating simulation, analytics, and digital twin capabilities, further enhancing innovation and efficiency. The automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment sectors were among the first to adopt PLM systems.
The history of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) in process manufacturing industries dates back to the late 20th century when the need for managing complex product formulations and regulatory compliance became increasingly evident. Initially, process manufacturers relied on basic document management systems to store and manage product information. Some companies also began using early forms of specification data management to handle product, regulatory, and manufacturing data. However, as product complexity and regulatory demands grew, these systems proved inadequate. The mid-2000s marked a significant shift with the development of PLM systems designed specifically for process manufacturing. These systems integrated formulation management, quality control, and regulatory compliance, addressing the unique requirements of industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and consumer goods. Specialized features were incorporated into PLM solutions to cater to the intricate needs of process manufacturers, enabling better collaboration, traceability, and lifecycle management.
Today, cloud-based PLM solutions are evolving, offering enhanced scalability, flexibility, and real-time access to data. Many of these solutions integrate advanced analytics, simulation, and digital twin technologies, enabling process manufacturers to optimize product development, improve quality, and accelerate time-to-market. These cloud-based systems provide a more robust framework for managing the entire product lifecycle, facilitating better collaboration, and ensuring up-to-date information is accessible from anywhere.

The synergy between PLM and ERP can be a game-changer, providing companies with a comprehensive framework to manage both product innovation and business processes. However, understanding their unique contributions and how they intersect is crucial for leveraging their full potential. This blog explores the fundamental differences and synergies between PLM and ERP, highlighting how each system supports various aspects of a business. By examining their roles, benefits, and integration strategies, we aim to provide a clear perspective on why both PLM and ERP are essential in today’s competitive landscape. Whether you are looking to enhance your product development capabilities or streamline your operations, understanding the interplay between PLM and ERP is key to driving sustainable growth and innovation.
What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software platform used by organizations to integrate and manage their core business processes in a unified system. ERP systems streamline and automate functions such as finance, human resources, procurement, inventory management, sales, and supply chain operations. By centralizing data and providing real-time insights, ERP solutions enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and facilitate better resource management across the organization.
For instance, in financial management, ERP systems help organizations manage transactions, general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting, ensuring data accuracy and regulatory compliance.
In supply chain management, ERP enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, demand forecasting, and optimized procurement processes, which reduces costs and improves efficiency. Human resources management benefits from ERP by streamlining payroll, employee records, recruitment, performance management, and benefits administration, enhancing data accuracy and compliance with labor laws. In sales and customer relationship management, ERP integrates CRM to provide a holistic view of customer data, improving customer service and driving sales effectiveness. Manufacturing operations are optimized through ERP by managing production schedules, work orders, and shop floor activities, leading to better coordination and product quality. Project management is enhanced with ERP by tracking timelines, budgets, resources, and milestones, ensuring successful project delivery. In procurement management, ERP streamlines vendor selection, purchase orders, contract management, and supplier performance monitoring, reducing costs and ensuring timely procurement.
Additionally, ERP systems support compliance and risk management by providing tools for monitoring compliance activities, conducting audits, and managing risk assessments, thus enhancing regulatory adherence and mitigating risks. Versatile and customizable, ERP systems meet the specific needs of various industries, providing a robust framework for managing and optimizing business processes across the organization.
How is ERP Different from PLM?
PLM systems are designed to manage the entire lifecycle of a product from conception through design, manufacturing, and disposal. Among the key capabilities discussed in this blog, Specification Data Management stands out as a core component of PLM. Whether capturing, evaluating, or enriching innovative ideas, or storing requirements as the basis of product development, Specification Data Management plays a critical role. It ensures consistency, quality, and compliance across all stages of product development and production. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date specifications, companies can avoid costly errors, reduce waste, and enhance product safety.
In industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, stringent regulatory requirements make precise specification management indispensable. It enables efficient collaboration among cross-functional teams, streamlines approval processes, and facilitates traceability and accountability. Additionally, robust specification management supports innovation by providing a clear framework for modifying and improving products. Ultimately, effective specification management not only safeguards a company’s reputation but also drives operational efficiency and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Another critical focus area of PLM is the creation of a recipe in process manufacturing or a Bill of Materials (BOM) in discrete manufacturing, which is essential for transforming conceptual designs into tangible products. A recipe or BOM serves as the foundational blueprint, detailing every raw material, component, and process step required to produce the final product. Accurate and comprehensive specification data underpin this entire process, ensuring that each ingredient or part meets the necessary quality standards and regulatory requirements. By integrating specification data into recipes or BOMs, companies can streamline product development, reduce errors, and enhance collaboration across cross-functional teams. This robust framework not only accelerates time-to-market but also ensures that the final product adheres to the desired design, functionality, and compliance standards, thereby driving innovation and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Handing over to manufacturing is another pivotal capability within Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) that ensures the seamless transition from product development to full-scale production. This process involves meticulously transferring detailed product specifications, manufacturing instructions, and quality criteria from the design and development teams to the manufacturing floor. Effective handover to manufacturing minimizes the risk of errors, misunderstandings, and delays, ensuring that the product is manufactured precisely according to the design intent. It encompasses the integration of Bill of Materials (BOM), recipes, and comprehensive work instructions, all underpinned by accurate and up-to-date specification data. By facilitating clear communication and collaboration between development and manufacturing teams, PLM ensures that products meet quality standards and regulatory requirements right from the first production run. This capability not only enhances operational efficiency and reduces time-to-market but also helps in maintaining consistency, improving product quality, and optimizing resource utilization, ultimately driving business success in competitive markets.
Beyond these critical capabilities, PLM encompasses several other key focus areas, including innovation management, requirements management, and supplier management. Innovation management within PLM involves fostering and managing new ideas, ensuring that they are efficiently developed and integrated into the product development process. This area is critical for maintaining a competitive edge, driving continuous improvement, and responding to market demands. Requirements management ensures that all product requirements, from customer needs to regulatory standards, are captured, analyzed, and tracked throughout the product lifecycle. This focus area is essential for aligning the final product with stakeholder expectations and compliance requirements. Supplier management within PLM ensures effective collaboration with suppliers, managing relationships, performance, and risk. It involves integrating supplier data and communication into the PLM system to enhance transparency, reduce lead times, and ensure the quality and reliability of supplied components. Together, these focus areas within PLM drive efficiency, innovation, and quality, enabling companies to develop superior products that meet market needs and regulatory standards while optimizing their supply chain and resources.
Service, maintenance, and obsolescence management are also integral capabilities within Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) that ensure the longevity and efficiency of a product throughout its entire lifecycle. PLM systems provide a structured approach to managing service and maintenance by capturing detailed product information, including service manuals, maintenance schedules, and historical performance data. This ensures that maintenance activities are performed accurately and efficiently, prolonging the product’s operational life and minimizing downtime. Furthermore, PLM facilitates the management of product obsolescence by tracking component lifecycles and predicting when parts will become obsolete, allowing companies to plan for replacements, updates, or redesigns proactively. This proactive approach helps in maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction while optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs associated with unexpected failures or obsolete parts. By integrating service, maintenance, and obsolescence management into PLM, companies can ensure continuous product support, enhance customer experience, and strategically manage the end-of-life phase, thereby sustaining product value and performance throughout its lifecycle.
In process manufacturing R&D community, many times definition of a “supplier” may mean manufacturer as opposed to the Procurement community definition of a “supplier”
For a detailed definition of PLM, its benefits, and the future of PLM, check out this blog.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) plays a critical role in integrating business functions and data across an organization by providing a centralized platform for managing core operations such as finance, human resources, procurement, inventory management, sales, and supply chain processes. ERP systems streamline these functions by ensuring that data from various departments is consistently and accurately captured, stored, and accessible in real-time. This integration facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across departments, enhances operational efficiency, and supports informed decision-making by providing a holistic view of the organization’s performance.
In contrast, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) specifically handles product data and specifications, managing the entire lifecycle of a product from conception through design, manufacturing, service, and disposal. PLM systems focus on ensuring product quality, innovation, and compliance by integrating data related to product development, design iterations, engineering changes, and regulatory requirements. By centralizing product-related information, PLM enables cross-functional teams to collaborate effectively, accelerates time-to-market, and ensures that products meet quality and regulatory standards.
While ERP integrates and optimizes business processes across the organization, PLM is dedicated to managing and improving the product development lifecycle. Together, they provide a comprehensive approach to managing both operational efficiency and product innovation, ensuring that an organization can effectively manage its resources while continuously delivering high-quality products.
Enterprise Resource Planning’s Impact on Product Development
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations must efficiently manage both their operational processes and product development lifecycles to achieve success. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems serve distinct yet complementary roles in this endeavor. Understanding how ERP integrates business functions and data, while PLM focuses on managing product data and specifications, is crucial for optimizing overall business performance and fostering innovation.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems significantly impact Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) by providing a structured framework for integrating business operations with product development processes. ERP systems streamline and automate core business functions such as finance, procurement, and supply chain management, which are essential for the successful execution of PLM strategies. By offering real-time visibility into resource availability, financial performance, and supply chain status, ERP systems enable better planning and execution of product development projects managed through PLM. This integration ensures that product designs and specifications are aligned with business constraints and operational capabilities, facilitating efficient resource allocation, cost management, and timely production. Additionally, ERP systems enhance data accuracy and consistency across the organization, supporting informed decision-making and reducing the risk of errors in product development and manufacturing. Moreover, the collaborative environment fostered by ERP systems improves communication and coordination between departments, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of PLM initiatives. The robust reporting capabilities of ERP systems also play a vital role in enhancing product quality and compliance by providing detailed insights and analytics on production processes, quality control measures, and regulatory adherence, ensuring that all aspects of product development and manufacturing meet the highest standards.

Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems impact ERP by providing detailed and accurate product data, specifications, and lifecycle information that are critical for effective business operations. PLM systems manage the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial concept and design to manufacturing, service, and disposal, ensuring that all product-related information is up-to-date and accessible. This comprehensive product data is essential for ERP systems to effectively manage procurement, production planning, inventory control, and quality assurance. By integrating PLM with ERP, organizations can ensure that product designs are accurately translated into manufacturing instructions and that any changes in product specifications are promptly reflected in production schedules and supply chain activities. This synergy enhances operational efficiency, reduces time-to-market, and ensures that products meet quality and regulatory standards. Ultimately, the integration of PLM and ERP creates a cohesive environment where product innovation and business operations are seamlessly aligned, driving overall organizational success.
Examples of ERP
SAP ERP: Widely used across various industries for its robust and comprehensive functionalities, covering finance, supply chain, procurement, and more.
Oracle ERP Cloud: Known for its extensive suite of applications that support enterprise functions such as financial management, procurement, and project management.
Microsoft Dynamics 365: Offers a range of applications that integrate ERP and CRM capabilities, ideal for small to large enterprises.
Integrating PLM and ERP Systems
PLM and ERP complement each other by bridging the gap between product development and business operations. PLM focuses on managing the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial concept and design to manufacturing, service, and disposal, ensuring product quality and innovation. Meanwhile, ERP handles core business processes such as finance, procurement, supply chain, and inventory management, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. By integrating PLM and ERP, organizations can ensure that accurate product data and specifications from the PLM system flow seamlessly into the ERP system, facilitating efficient production planning and resource management. This integration enhances collaboration across departments, reduces errors, and accelerates time-to-market for new products. Ultimately, the synergy between PLM and ERP provides a holistic approach to managing both product innovation and business processes, driving overall organizational success.
Benefits of Integrating PLM and ERP Systems
The integration of PLM and ERP systems hinges on crucial master data points such as the material master and Bill of Materials (BOM), with PLM typically serving as the source system for these data sets. The material master in PLM contains detailed specifications and characteristics of raw materials and components, which are essential for ensuring product quality and consistency. This data is seamlessly transferred to the ERP system, where it supports procurement, inventory management, and production planning. Similarly, the BOM, which outlines the hierarchical structure of a product’s components and subassemblies, originates in the PLM system and is fed into the ERP system to guide manufacturing processes.
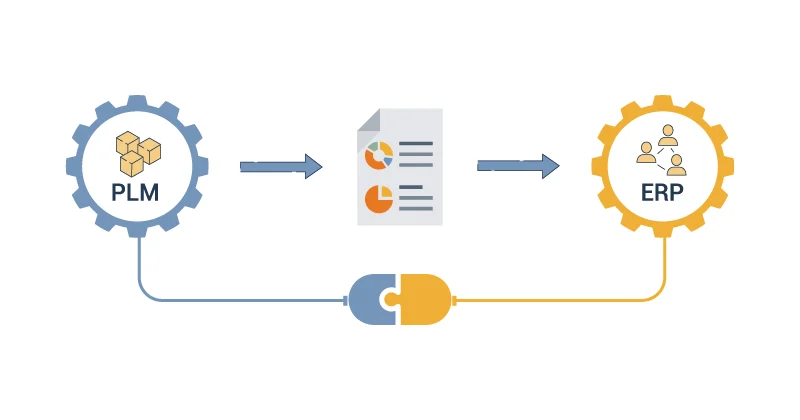
Additionally, PLM can generate manufacturer and supplier data, providing critical information about sourcing, compliance, and quality standards. This integration enhances upstream and downstream visibility for all stakeholders, allowing for better coordination and informed decision-making. The improved visibility ensures that accurate, up-to-date information flows across the enterprise, enhancing collaboration between product development and operational functions, ultimately driving efficiency, reducing time-to-market, and fostering innovation.
Integration Best Practices
The integration of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems hinges on critical master data points such as the material master and Bill of Materials (BOM). The material master, containing detailed specifications and characteristics of raw materials and components, and the BOM, outlining the hierarchical structure of a product’s components and subassemblies, are typically sourced from the PLM system and transferred to the ERP system to support procurement, inventory management, and production planning. A crucial aspect business must consider during this integration is change management. Ensuring that any updates or modifications in product design or specifications within the PLM system are accurately and promptly reflected in the ERP system is vital to maintain consistency and prevent errors. Since the BOM resides in the ERP system, changes to the BOM that deviate from the prescribed range set by R&D can significantly affect product quality, product stability, and regulatory compliance. Effective change management processes facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between departments, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of and can act upon the latest product information. This not only enhances operational efficiency and product quality but also reduces the risk of costly disruptions and delays, ultimately driving business success.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems is crucial for optimizing business performance. PLM focuses on managing the entire lifecycle of a product—from conception, design, and manufacturing to service and disposal—ensuring innovation, quality, and regulatory compliance. Conversely, ERP integrates various business functions such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and manufacturing into a unified system, streamlining processes and enhancing operational efficiency. The synergy between PLM and ERP allows for seamless data flow and collaboration across departments, enhancing decision-making and reducing time-to-market for new products. By integrating PLM’s detailed product data and specifications with ERP’s comprehensive business operations, organizations can drive efficiency, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Specright offers a robust Specification Data Management (SDM) and formulation solution that can seamlessly integrate with leading ERP systems such as SAP and Oracle. This integration ensures that detailed product specifications, formulations, and regulatory compliance data are accurately and efficiently managed throughout the product lifecycle. By connecting Specright’s advanced solutions with ERP systems, companies can establish a single source of truth, enhancing data accuracy and consistency across the organization. The user-friendly interface and comprehensive functionality of Specright’s solutions improve user experience, making it easier for teams to collaborate and access critical information. This integration streamlines procurement and manufacturing processes, ensures consistent product quality and compliance, and empowers organizations to optimize their operations, reduce errors, and accelerate time-to-market, ultimately driving innovation and operational excellence.
If you’d like to learn more or see a demo live you can request a demo here.
Explore More Blogs
Get Started
With Specright’s Solution Suite, you can digitize, centralize, and link your specification data to drive efficiencies, intelligence, traceability, and collaboration within your organization and across your supply chain network.




